What’s the Difference Between Cannabinoids & Terpenes?

The Cannabis Sativa plant has been used for centuries in natural remedies, yet it’s only recently that scientists have focused their research on the plant’s unique compounds, terpenes and cannabinoids.
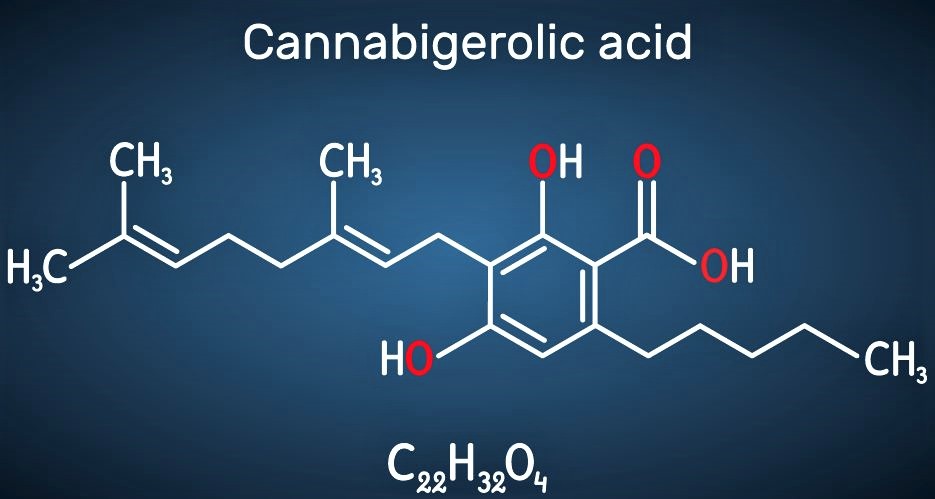
Currently, scientists are very interested in learning more about the plant’s 100+ cannabinoids, and some people believe the properties of cannabinoids can be enhanced by terpenes commonly referred to as the entourage effect. (Learn more about the entourage effect.)
What are Terpenes?
Terpenes are the largest and most diverse group of naturally occurring compounds known to date. It’s currently believed that there are at least 20,000 different terpenes in existence, most of which are found in plants.
All terpenes have a similar chemical structure and are classified as “aromatic compounds” due to their odor, which is distinctive to each plant. For example, the smells of pine as you walk in the woods, the soothing fragrance of lavender, even the unmistakable odor of an orange, are all due to each species’ unique mix of terpenes. These compounds give plants their signature scent and are the key components of many plant-based essential oils. Plants use these aromas to attract pollinators and discourage scavengers, making terpenes essential to their survival.
How are Cannabinoids and Terpenes Different
From what we know so far, terpenes may not be that different from cannabinoids. Structurally, the compounds are somewhat similar, and some scientists have hypothesized that terpenes may bind to many of the same receptors in the human body as cannabinoids. Research is ongoing.
Also similar to cannabinoids, terpenes have been widely used as natural remedies for enhancing the ability to sleep and acting as anti-inflammatories and antioxidants. For example, curcumene, a component of turmeric is a terpene. It’s one of the compounds in turmeric thought to provide anti-inflammatory and antioxidant benefits.
Another everyday ingredient that is also a terpene is menthol, which is found in peppermint and spearmint plants. It’s known for it’s cooling abilities and is used in many everyday products such as toothpaste.
Beta Carotene found in carrots and other orange vegetables is also a terpene. It breaks down into Vitamin A and is known for its antioxidant properties.
Understanding the Role of Terpenes
Scientists have been studying terpenes and there is a lot of information available. However, with over 20,000 unique compounds, and understanding several work together to provide a therapeutic effect, there is still much work to be done.
Currently, there is a lot of movement studying the terpenes found in the cannabis plant to understand their potential benefits including:
Myrcene
· Found in thyme, mango and lemongrass.
· It is thought to have analgesic and sedative properties.
Limonene
· Found in lemon rind, orange rind, and juniper. It gives citrus fruits their distinct smells.
· Some data indicates it may have anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-stress effects.
Caryophyllene
· Found in black pepper, cloves and cinnamon.
· Caryophyllene was shown in some studies to selectively bind to cannabinoid receptor 2 making it the only terpene, to date, shown to interact with the endocannabinoid system. It is thought to have anti-inflammatory properties, but more research is needed.
Terpinolene
· Found in lilac, nutmeg, and cumin.
· It has been used historically as a sedative and some people believe it has antioxidant, antiseptic, antifungal, and antibacterial properties.
Pinene
· Found in pine needles, rosemary and basil.
· It may exhibit anti-inflammatory and anti-anxiety properties but additional data is needed.
Humulene
· Found in hops, and wood.
· It is suspected to have anti-inflammatory, and anti-bacterial properties.
Ocimene
· Found in mint, parsley, and orchids.
· Further exploration is needed to determine if it has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
Linalool
· Found in lavender and birch bark.
· It is thought to have anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antimicrobial properties. Additional studies are needed.
The Potential of Terpenes
Scientists are aware that terpenes have potential as medicinal products.
Paclitaxel (Taxol), a prescription medication approved for treating certain types of cancer including ovarian cancer is a terpene derivative. And more products based on terpenes are currently being researched.
Both cannabinoids and terpenes may have benefits that can improve the lives of people around the world and we are excited by the emerging science and research behind both.
Here, at Demetrix, we are unlocking the potential of cannabinoids as ingredients and their health and wellness benefits – follow us on LinkedIn and Twitter to learn more.